Microneedles as alternative to conventional drug administration
Commonly used methods of drug delivery are associated with certain drawbacks: As an example, injections are invasive and, thereby, usually painful. Microneedles, though, as an alternative to conventional routes of drug administration, penetrate only the outermost layer of the skin without pain, and applying them with patches may not require the assistance of trained medical personnel.
By releasing their active ingredients into the epidermis and/or superficial dermis, bioactive molecules are administered locally, targeted, and effectively. Various types of microneedles have been developed for specific application cases.
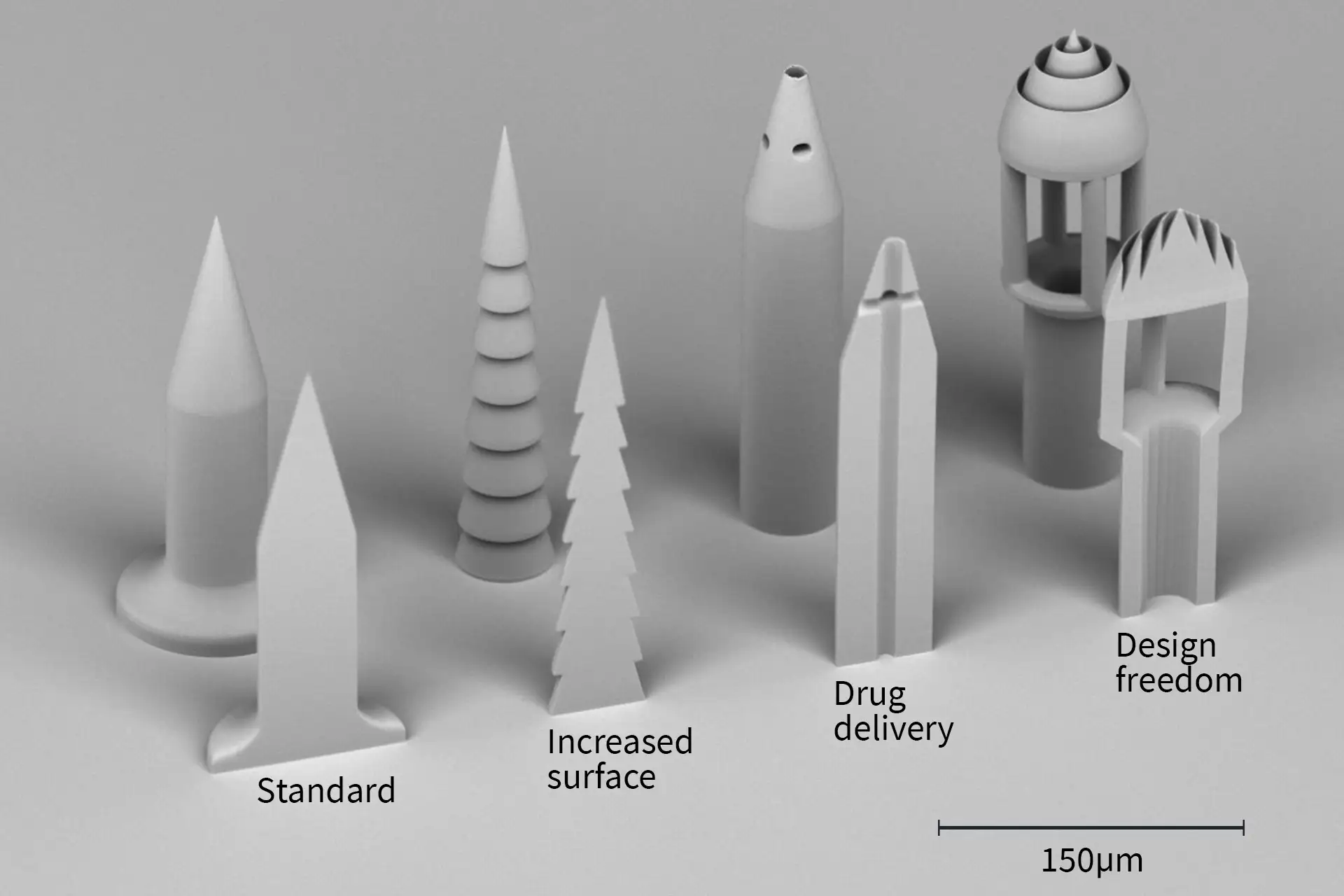

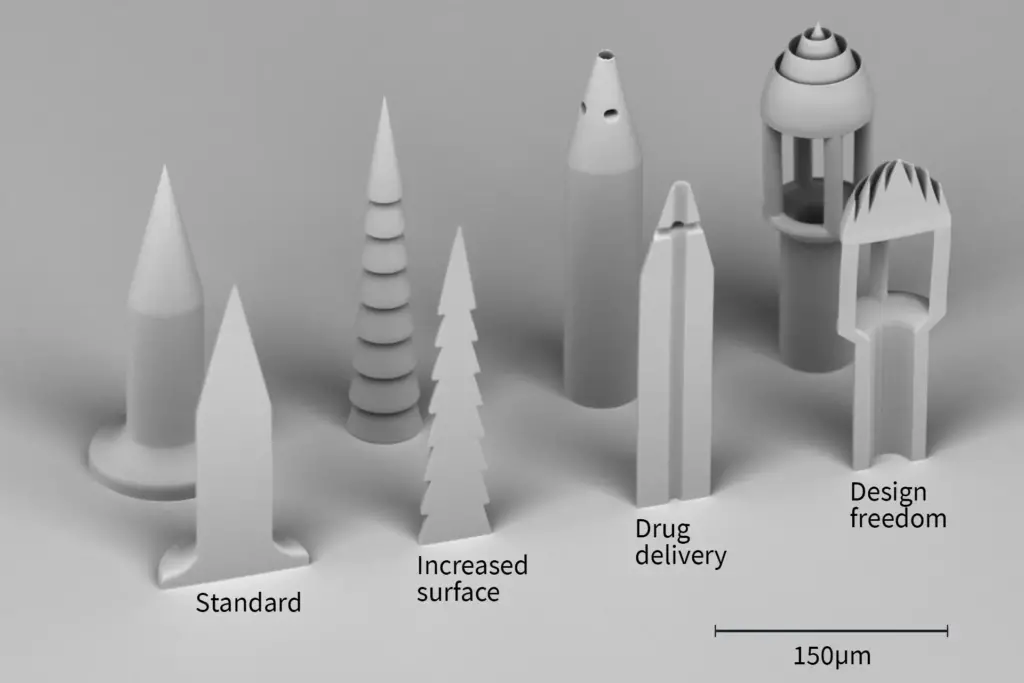
- Solid needles puncture the skin to create openings. The microneedles are then removed and replaced with a drug-containing patch, allowing for drug distribution via the pathway established by the microneedles. (left)
- The surfaces of solid microneedles are coated in the drug, enabling drug dissolution upon insertion into the skin. The individual needle can be designed with an increased surface to allow for more of the drug to be administered at once. (second from the left)
Alternatively, the microneedle patch is scraped across the skin, leaving the drug in the abrasions.
- Another approach are hollow microneedles, designed to have the drug solution filled into their empty space. (second from the right)
- Furthermore, drugs can be incorporated into a biodegradable polymer. The microneedles fabricated from this polymer then dissolve within the skin, releasing their active ingredients in the process.
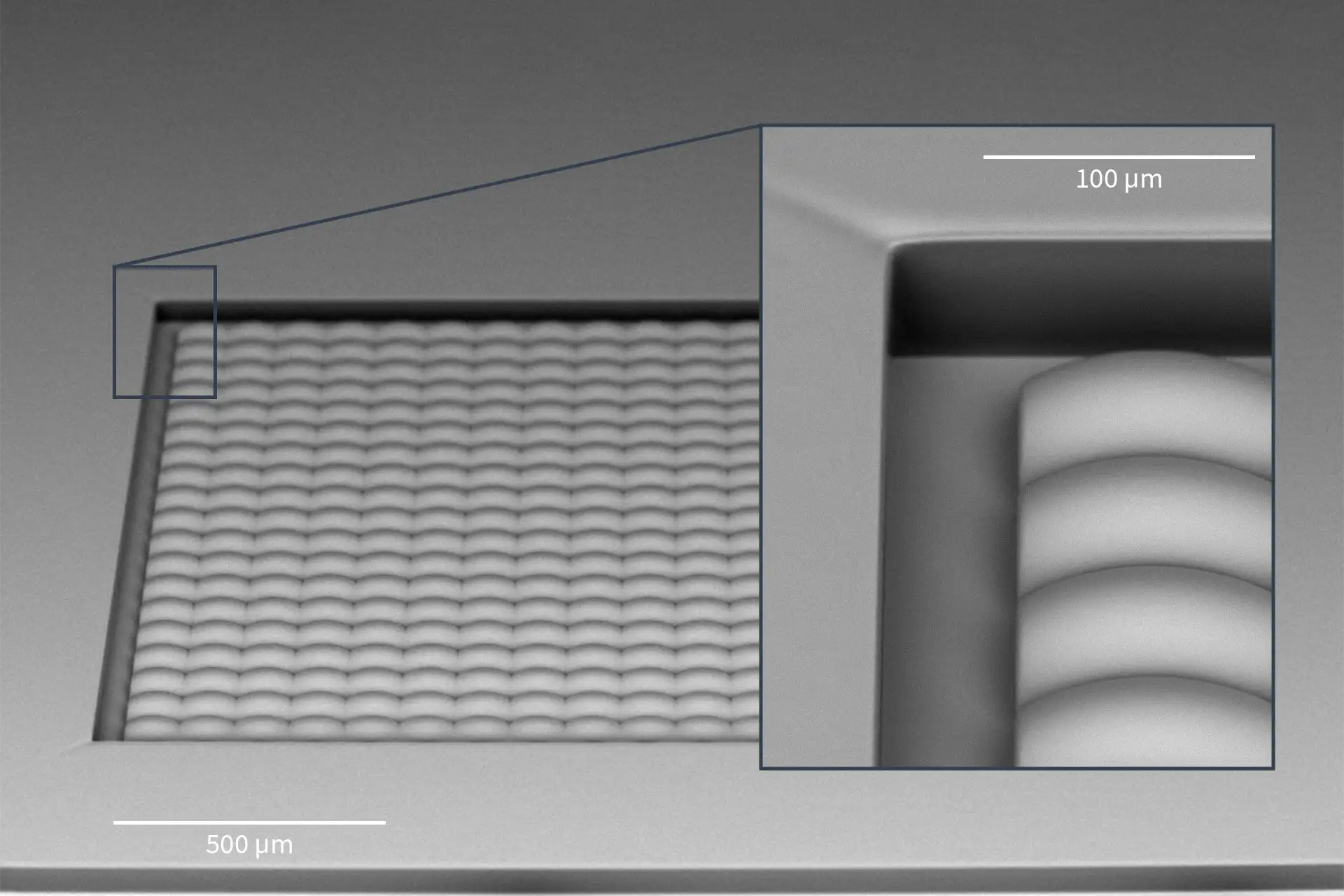
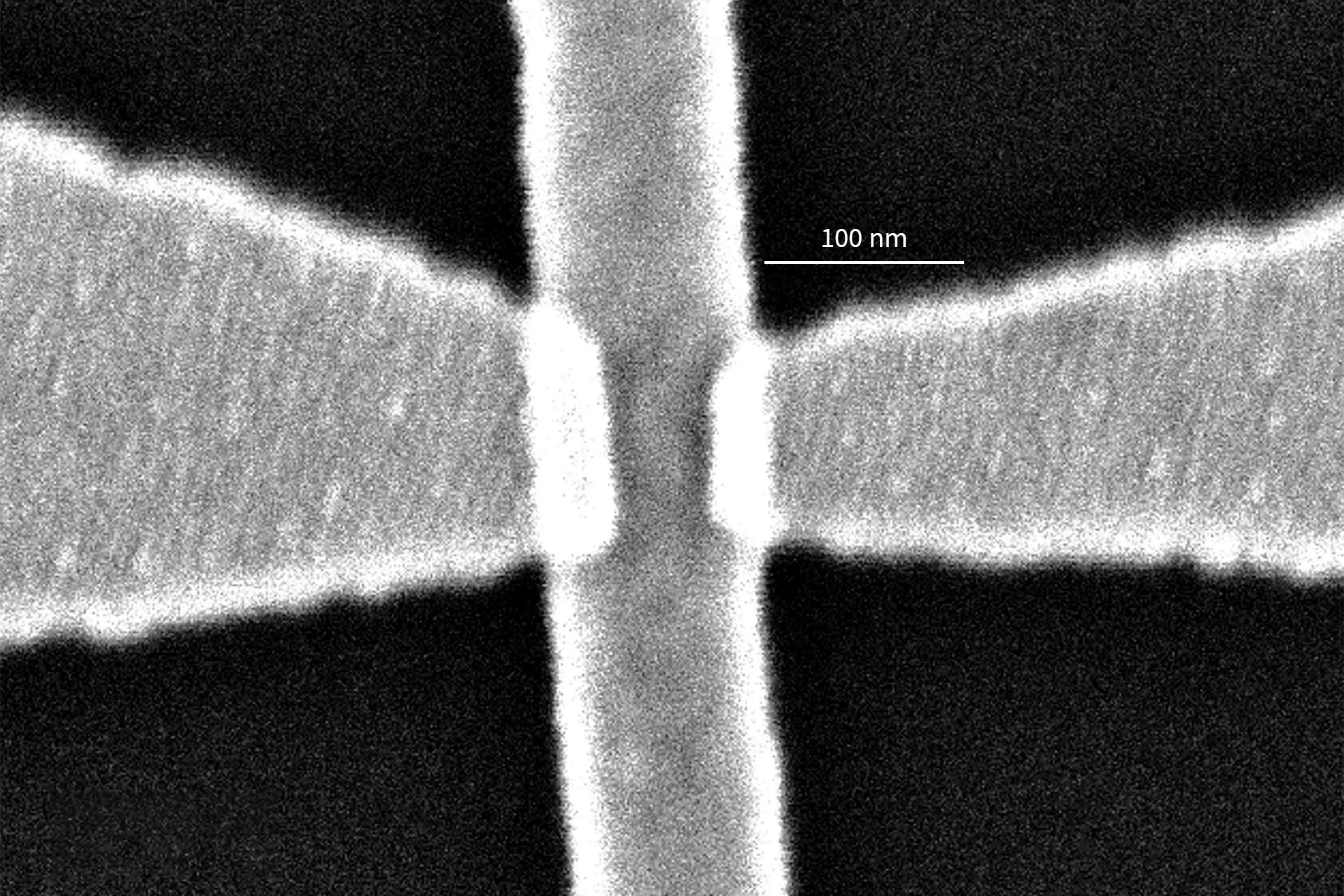
- Our 3D Lithography and 3D Microprinting tool MPO 100 enables you to fabricate those microneedles for drug delivery with a high level of design freedom (right) and directly into the substrate with high precision and accuracy.
Learn more about the
Contact us for
Stay updated and subscribe to our news:
General information for this post has been sourced from:
Microneedles: A smart approach and increasing potential for transdermal drug delivery system
Stimuli-responsive transdermal microneedle patches