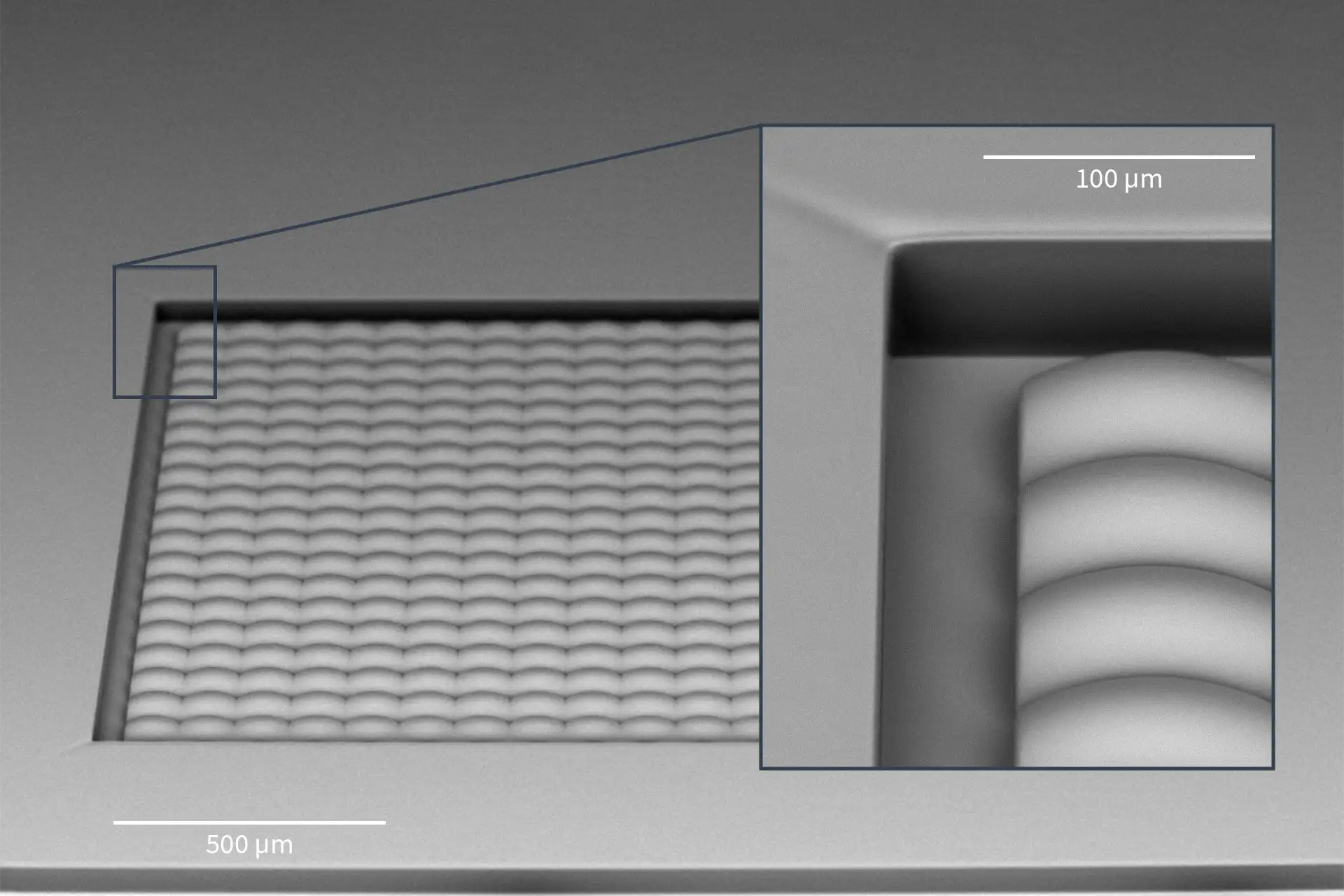
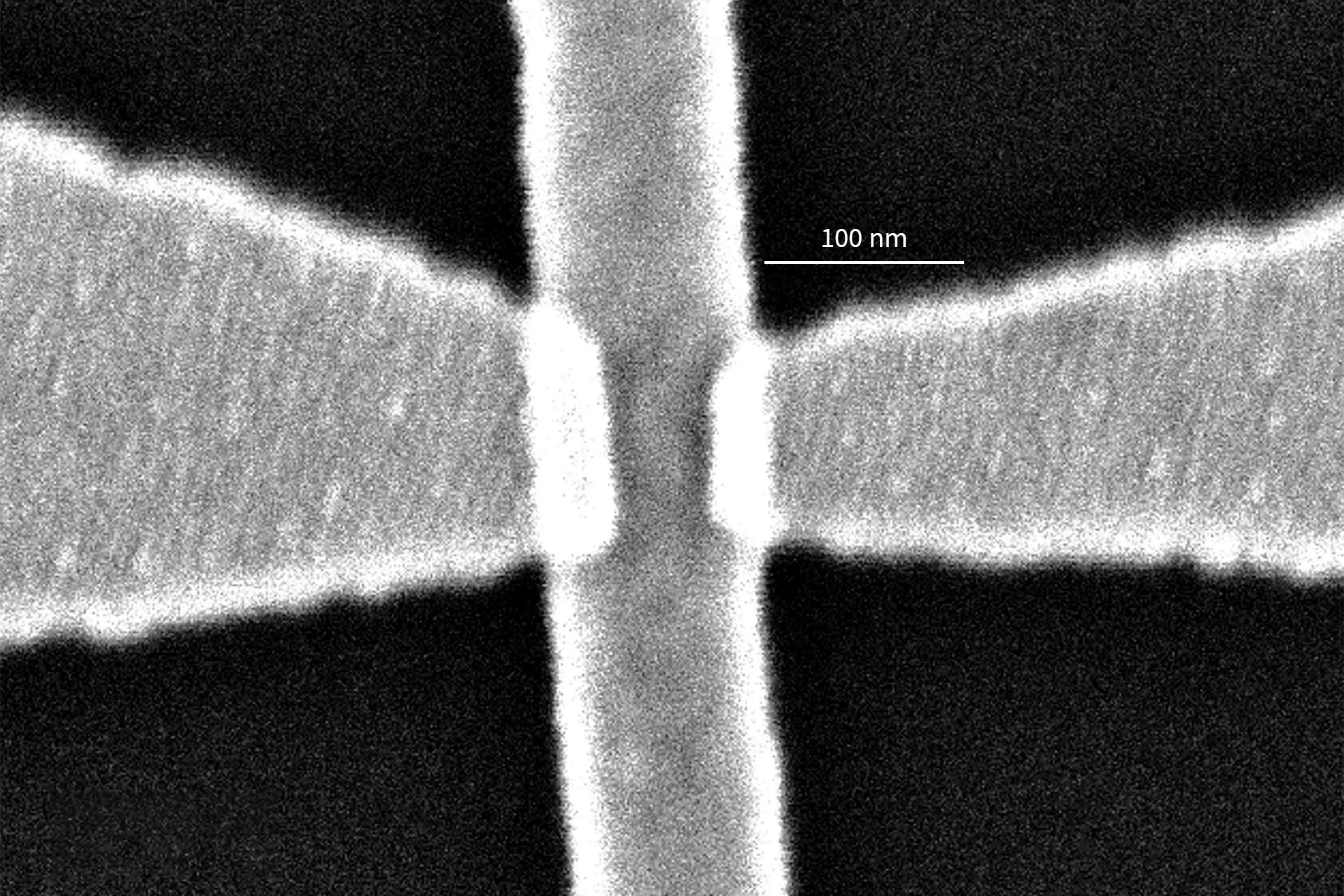
NanoFrazor can be used to locally induce heat-driven phase changes. Dr Ann-Katrin U. Michel and her colleagues from ETH Zürich and RWTH Aachen University are exploring this capability. They proposed a new technique for fabricating near-infrared metasurfaces with feature sizes far below the diffraction limit. Their results were recently published in Advanced Optical Materials.
Phase-change materials such as GeTe, which was the material used in this work, have distinctly different properties depending on whether they are in their crystalline or amorphous state. The heat from the NanoFrazor’s tip drives crystallization of a small volume of the material under the tip. The resulting array of few-nm-sized crystalline dots in amorphous GeTe would significantly change the wavelength at which the resulting metasurface absorbs the light.
In this work, the authors designed a perfect absorber for the near-infrared spectral range. These wavelengths are typically used in telecommunications, so such devices could prove very useful for currently existing technology. A similar approach can also be used for other optics and biosensing applications.